When it comes to selecting the best windows for your home or building, uPVC windows have become the top choice for their durability, energy efficiency, and low maintenance. Among the various options available, glazing is a critical factor in determining the performance of the windows, with single, double, and triple glazing offering distinct advantages.
This guide will explore the differences between these glazing types, along with the benefits, costs, and performance considerations to help you make an informed decision for your next window installation.
uPVC Frames
Material: Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride (uPVC)
uPVC is a type of rigid plastic that is known for its resistance to weathering, corrosion, and rot. Unlike traditional wood or metal frames, uPVC does not require frequent maintenance, such as painting or sealing. This makes it a popular material choice for window frames.
Benefits
- Durability: uPVC frames are highly resistant to moisture, UV rays, and extreme temperatures, ensuring longevity without the need for regular repairs or maintenance.
- Energy Efficiency: uPVC is a good insulator, helping to keep homes warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
- Low Maintenance: The material doesn’t need to be painted or treated regularly, saving you both time and money.
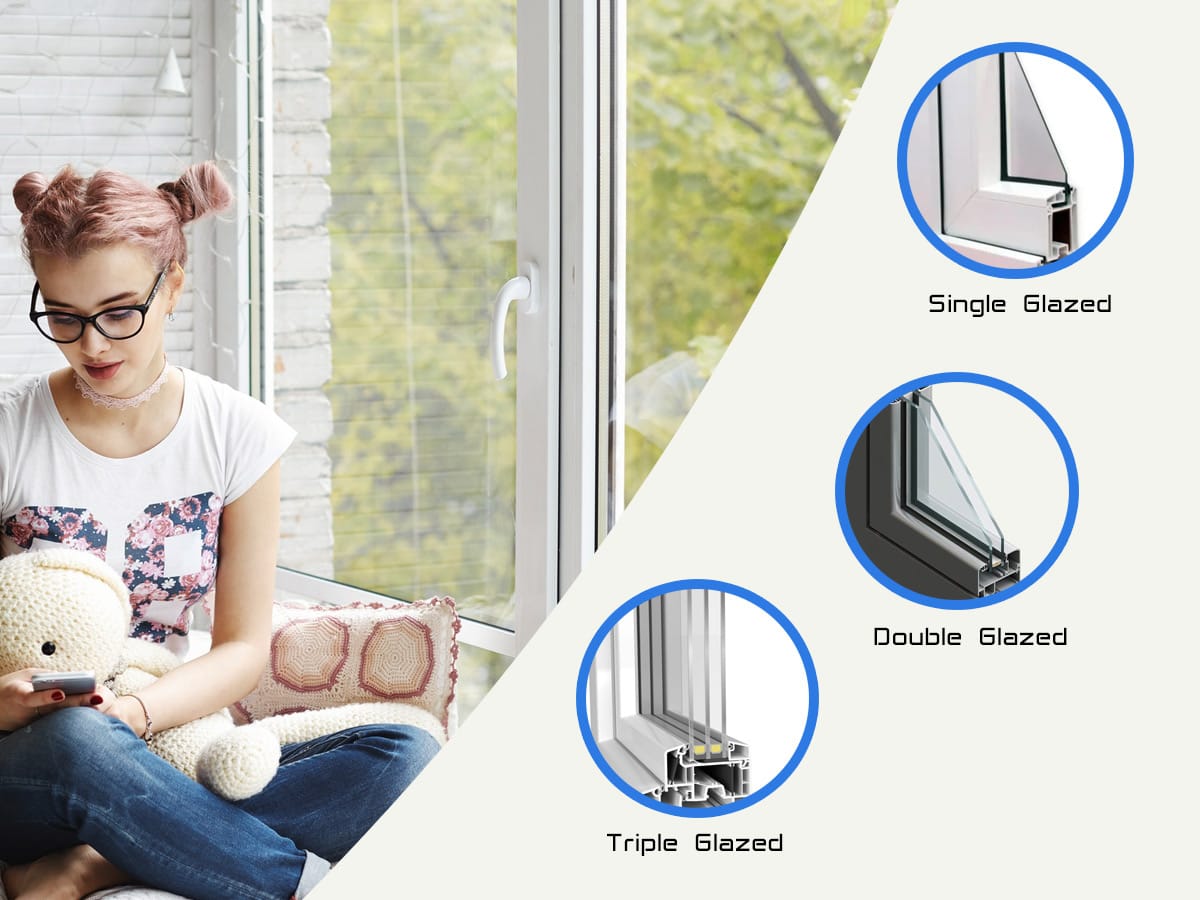
Types of Glazing
Glazing refers to the number of glass layers used in a window. The more layers there are, the better the thermal insulation and noise reduction. Let’s break down the different glazing types available.
Single Glazed
A single-glazed window is made up of just one pane of glass within the uPVC frame. While this is the most basic option, it has some performance limitations.
Double Glazed
A double-glazed window consists of two glass panes with a sealed gap between them, often filled with air or gas to enhance insulation. This type is the most commonly used option for modern homes.
Triple Glazed
Triple glazing involves three glass panes with two sealed gaps filled with gas. This provides superior thermal insulation and noise reduction, making it ideal for colder climates or high-noise environments.
1. Single Glazed uPVC Windows
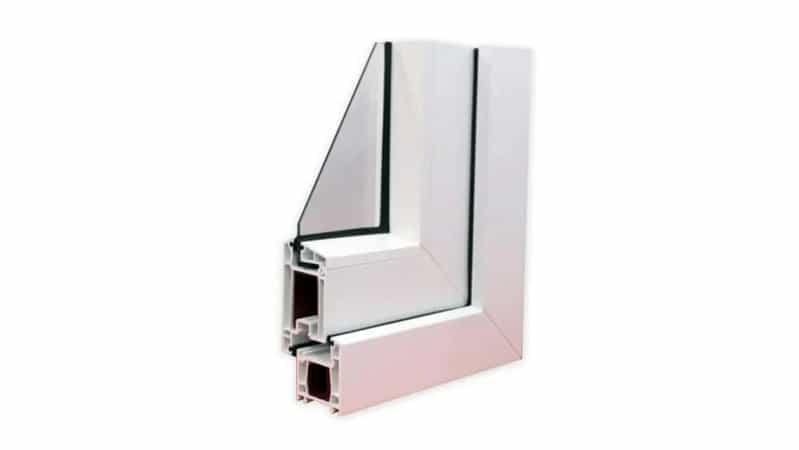

Structure
A single-glazed window uses just one pane of glass, offering the simplest and most cost-effective option.
Performance
- Thermal Insulation: Single glazing offers minimal insulation, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Noise Reduction: Single-glazed windows allow more noise to penetrate from the outside.
Use
- Ideal For: Older buildings, budget-conscious projects, or climates with moderate temperatures.
- Drawbacks: Increased risk of condensation, poor energy efficiency, and vulnerability to external noise.
2. Double Glazed uPVC Windows
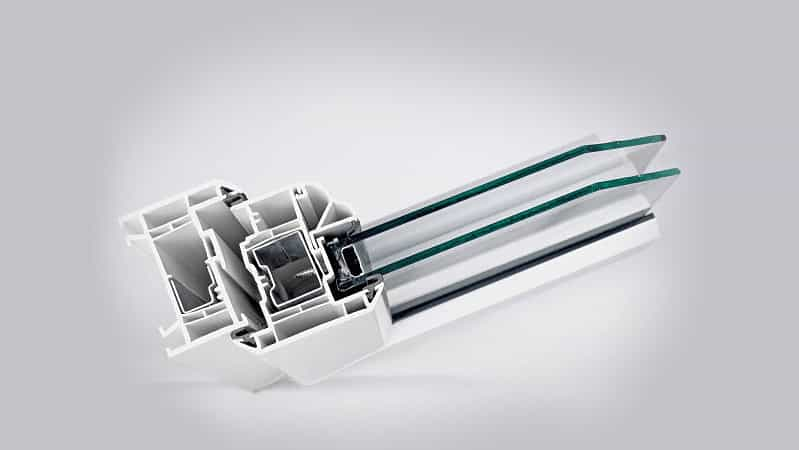
Structure
A double-glazed window contains two panes of glass separated by an air or gas-filled cavity, improving insulation.
Performance
- Thermal Insulation: The air gap or gas-filled space between the panes reduces heat transfer, offering better energy efficiency.
- Noise Reduction: Double glazing provides a 20-30% reduction in noise compared to single glazing, making it ideal for most residential homes.
Use
- Ideal For: Standard homes, commercial buildings, and areas with moderate climate conditions.
- Drawbacks: While more energy-efficient than single glazing, double glazing is slightly more expensive.
3. Triple Glazed uPVC Windows
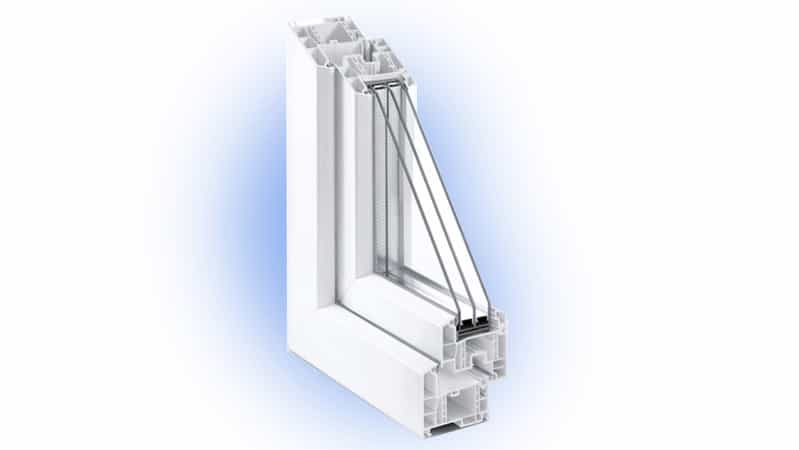

Structure
Triple glazing features three panes of glass with two cavities filled with gas, providing even greater insulation.
Performance
- Thermal Insulation: Triple glazing can improve thermal insulation by up to 50% compared to double glazing, making it ideal for extreme climates.
- Noise Reduction: Triple-glazed windows offer superior noise reduction, which is especially useful in high-traffic areas or near airports.
Use
- Ideal For: Homes in colder climates, luxury properties, and environments with significant noise pollution.
- Drawbacks: Higher cost and heavier frames that may require additional structural support.
Key Considerations for Choosing Glazing
When selecting the best glazing option for your windows, consider the following factors:
- Energy Efficiency: More layers of glass help retain heat, reducing energy costs.
- Cost: Triple glazing is the most expensive upfront but may save money in the long term due to its energy efficiency.
- Weight: Triple-glazed windows are heavier, requiring stronger frames and structural support.
- Condensation: Multi-glazed windows reduce condensation and moisture buildup inside your home.
Energy Efficiency in uPVC Windows
The energy efficiency of windows is crucial in determining the overall heating and cooling costs of a home. uPVC frames with double or triple glazing provide excellent insulation, ensuring that your home stays warm during the winter and cool during the summer. The gas-filled cavities between glass panes help to prevent heat transfer, keeping your energy bills low.
Cost Comparison of Glazing Types
- Single Glazing: The most affordable option, suitable for budget projects and temporary structures.
- Double Glazing: Slightly more expensive than single glazing, but offers better insulation and energy savings.
- Triple Glazing: The most costly option upfront, but the improved thermal efficiency and noise reduction can provide significant long-term savings.
Weight Considerations for uPVC Windows
Triple-glazed windows are significantly heavier than single or double-glazed windows, which means the frames need to be more robust to support the added weight. Ensure that your home’s structural framework is capable of supporting the additional load.
Condensation and Moisture Control
Condensation can lead to mould and mildew growth, which is why reducing moisture buildup is essential. Multi-glazed windows, particularly double and triple glazing, reduce condensation by keeping the inner glass panes warmer, preventing water droplets from forming.
Uses
Uses of Single Glazed uPVC Windows
Single-glazed windows are commonly used in renovation projects for historic buildings or temporary structures where cost is a major factor. They are also suitable for regions with mild climates where insulation is less of a concern.
Uses of Double Glazed uPVC Windows
Double-glazed windows are the most common choice for residential homes and commercial buildings. Their energy efficiency, noise reduction, and moderate cost make them suitable for a wide range of environments.
Uses of Triple Glazed uPVC Windows
Triple-glazed windows are perfect for areas with harsh winters, such as Nordic climates, or homes located near noisy environments like airports. They are also a good choice for energy-efficient and eco-friendly home designs.
Final Thoughts
Each type of glazing offers its own set of benefits, and the right choice depends on your specific needs. Single glazing is cost-effective for budget projects, while double glazing strikes a balance between performance and cost. For extreme climates or noise-sensitive areas, triple glazing is the best option, offering superior thermal insulation and soundproofing.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between single, double, and triple glazing?
Single glazing uses one pane of glass, while double and triple glazing use multiple panes with gaps filled with air or gas to improve insulation.
2. Which is the most energy-efficient glazing option?
Triple glazing provides the best insulation, followed by double glazing. Single glazing is the least energy-efficient.
3. Are triple-glazed windows worth the extra cost?
Yes, especially for homes in cold climates or high-noise areas, as they provide better insulation and soundproofing, potentially saving money in the long run.
4. Can I replace my single-glazed windows with double or triple glazing?
Yes, it’s a common upgrade for improving energy efficiency and reducing noise.
5. Do double-glazed windows reduce noise?
Yes, double-glazed windows offer significant noise reduction compared to single glazing.
6. How long do uPVC windows last?
uPVC windows can last for up to 30 years or more with minimal maintenance, especially when paired with double or triple glazing.

